A typical use of RW Net is to create isochrones around one or more center facilities. This can be based on either time or distance (or more generally cost). When such an isochrone is calculated, the cost is only defined on the street network itself. But typically there is a wish to have the isochrone presented as a polygon layer, often with thematic colours.
Many approaches can be used to transform the link-based results into polygons, but it is not possible to create a transformation, which will be acceptable in every single scenario - simply because it isn't clear what the cost is once you leave the road and what street segment you want to start from.
In RW Net the "off-road" cost is 0, so that "the cost inside a drivetime polygon somehow describes the cost of driving from the nearest road to the target facility". The nearest road does, however, not always has to be the one with the lowest cost !
In RW Net an approach is chosen which uses voronoi polygons created around the nodes in the street network. This is a very fast method, but has some drawbacks in the case of long street sections without any breaks / nodes. To make the result more correct, it is possible to dynamically add additional nodes along long street sections (AddNodes).
Calculation of the voronoi polygons uses 2D formulas for the trigonometric calculations, so isochrones based on spheric coordinates will not be 100% correct, but it is unlikely that this will ever be a problem for normal use.
See also function IsoPoly2, IsoPoly3, IsoPoly4 and property AddNodes.
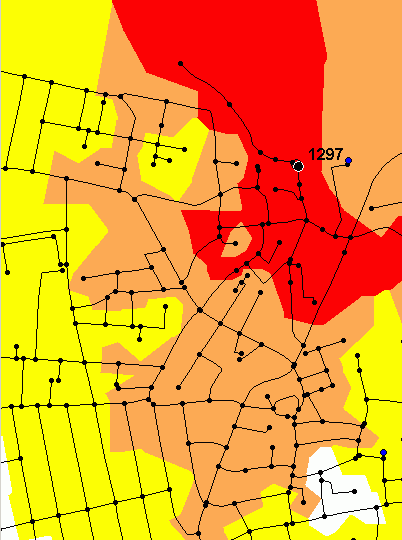
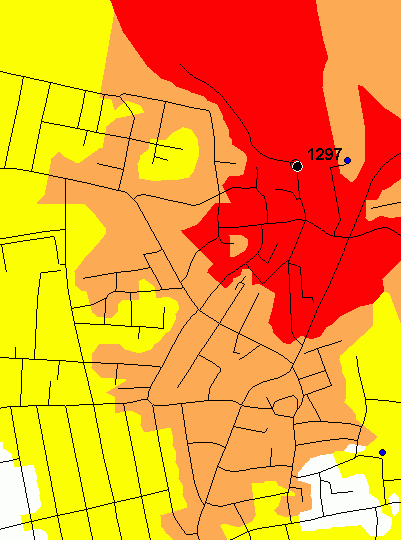
Below you can see 2 maps. The first shows an isopoly2 calculation with isochrones at 1, 2 and 3 km. Only the true nodes of the network has been used in the calculation (shown on the map). On the second map, additional nodes for every 50 meters has been added and a more exact and smooth polygon is the result.